Chapter 2 of 6
Import and Contouring
The treatment planning process for each patient begins with importing and localizing the CT images into the treatment planning system.
Following simulation, the CT dataset is imported into the Treatment Planning System. These images are in DICOM format, and you may hear this collection referred to as the DICOM import folder.
Once imported, the CT scan is utilized to localize the patient within a coordinate system and markings, enabling precise tracking of the patient’s geometric position in space.
During simulation, patients are often marked to aid in setup reproducibility during treatment. Small radiopaque markers, commonly referred to as BBs, are typically placed in a triangular configuration at three points (anterior and bilateral lateral positions). This location is designated as the user origin or localization point.
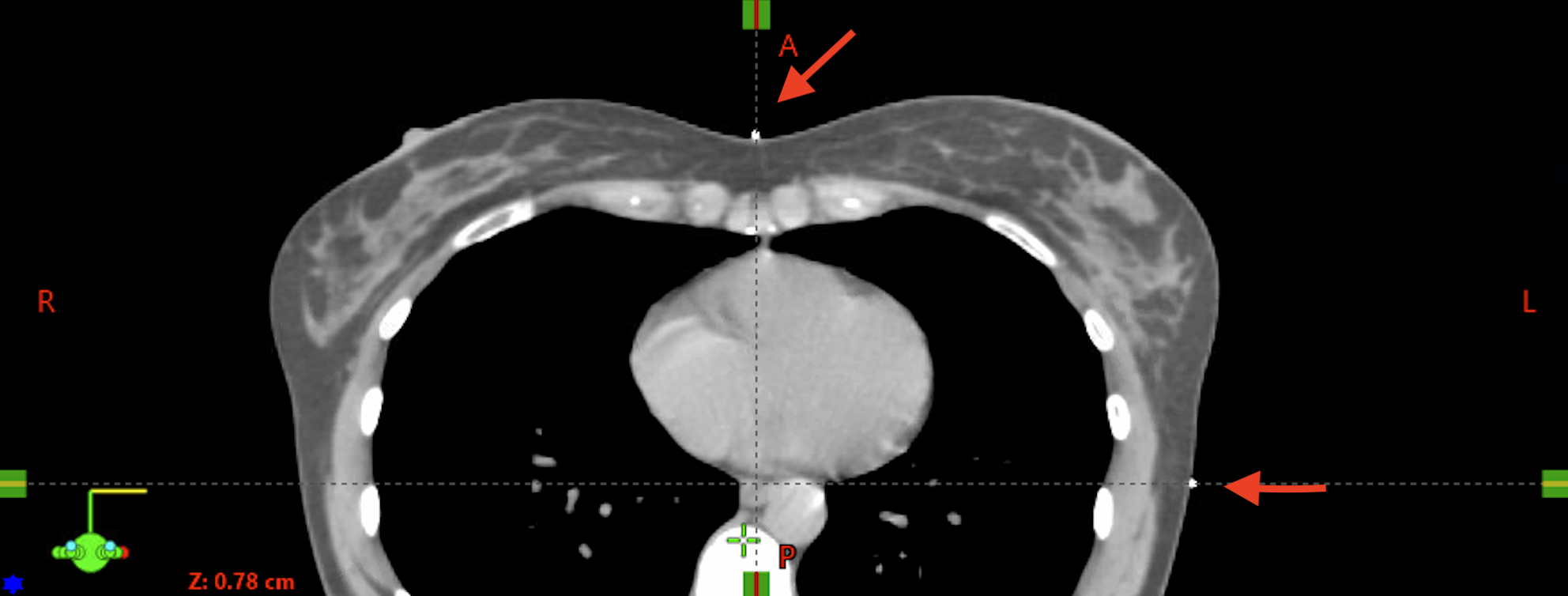

Three-Point Setup for Breast
An alternative approach is to align the patient using the anterior marker. Each institution may have its preferred method for breast setups.
Anterior Marker Used for Breast Setup
Contouring
Contouring of Setup BBs
Field Border Wires Used for Field Setup
Scar Wires Used to Mark the Surgical Incision Location
For this treatment, the physician has delineated the Clinical Target Volume (CTV)/Lumpectomy Cavity as our target volume, as illustrated below.
CTV/Lumpectomy Cavity Designated as a Target
The following structures are additional contours commonly used in breast treatment planning.
Any Critical Structures?
Contour any additional critical structures relevant to the specific case.
Density Overrides
If artifacts or other materials require density adjustments, this is an appropriate stage to apply overrides.
Summary
Always review automated contours carefully and ensure a second reviewer verifies your work.
With the contouring process complete, we are now prepared to proceed to treatment planning.
Next: Beam Setup

