Chapter 1 of 6
Simulation is a process that enables radiation treatment to be delivered in a reproducible manner. The simulator is a computed tomography (CT) scanner. The CT images are utilized to delineate targets and organs at risk, allowing the dosimetrist or physician to arrange radiation beams and develop a customized treatment plan. Special care is taken to ensure the patient’s comfort, facilitating consistent positioning for each treatment session. Some key considerations for whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) planning include:
- Imaging: CT scan, typically with a slice thickness of ≤ 3 mm
- Position: Supine
- Head immobilization
- Technique: 3D CRT
- Image-guidance
Immobilization
For WBRT treatment, a variety of commercially available head immobilization devices are used, most commonly thermoplastic masks with a custom headrest. For more precise positioning, which is generally not required for whole-brain radiotherapy, a more rigid stereotactic thermoplastic mask may be employed.
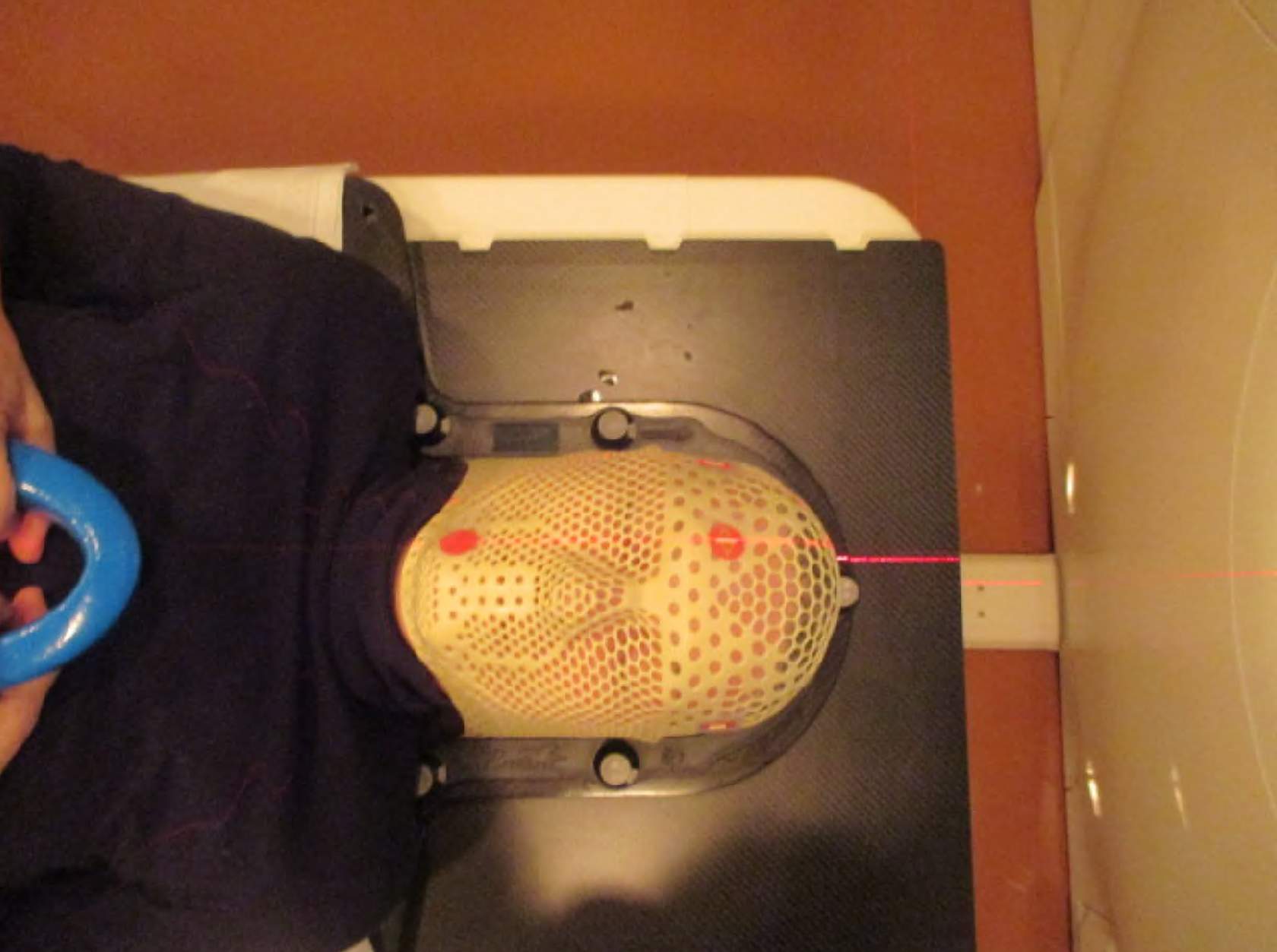
For CT simulation involving the brain, the patient is placed in the immobilization device and scanned. The isocenter or reference markers are selected and marked on the thermoplastic mask.


Simulation
Mask Markings (BB)
After the markings on the mask are made, therapists will take several photographs of the patient in the simulation position. These photographs and marks will serve as guides to position the patient correctly each day during treatment.
Markings are typically marked on the patient’s mask, as shown above.
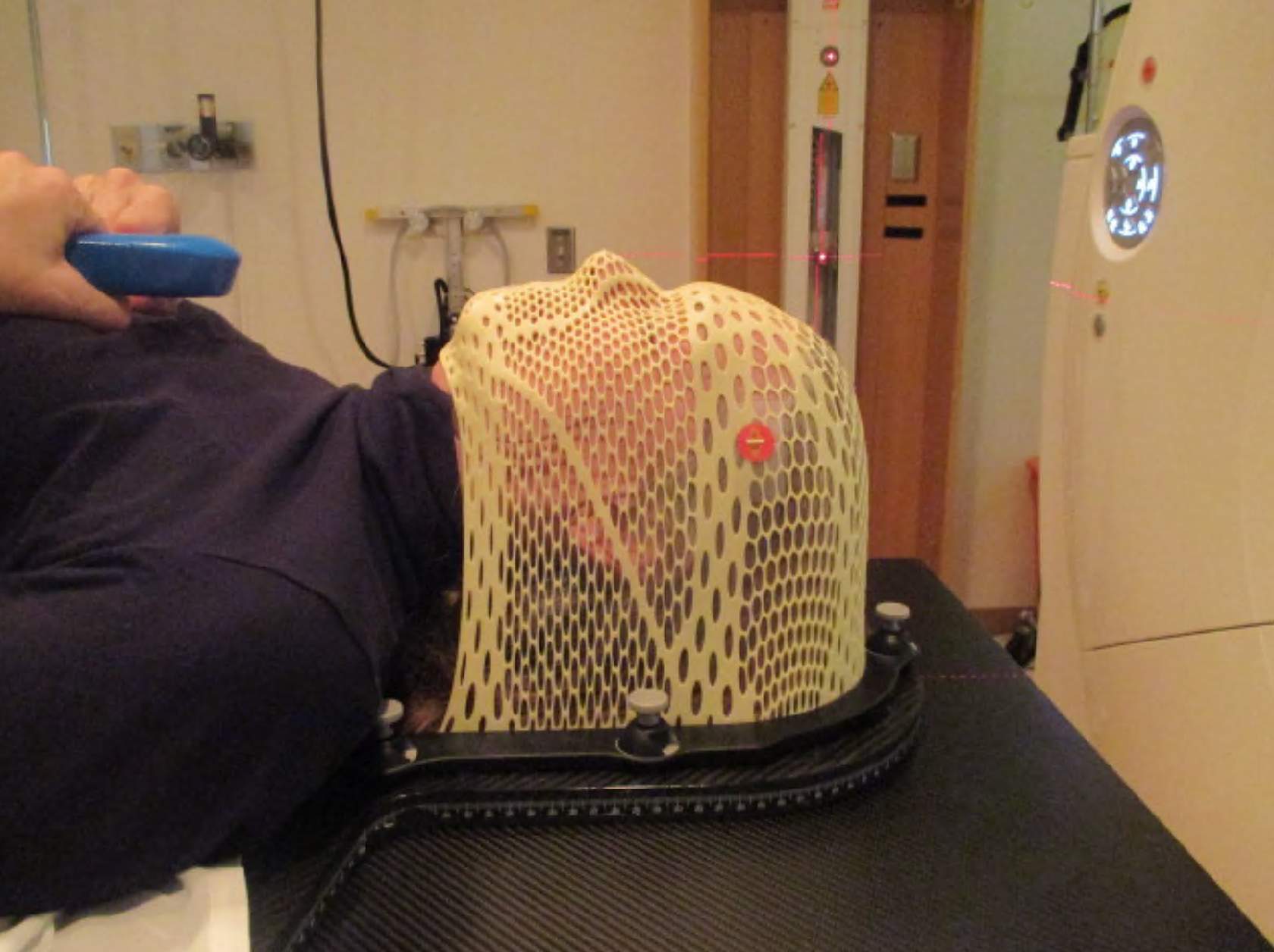

Mask: 5-Point Mask
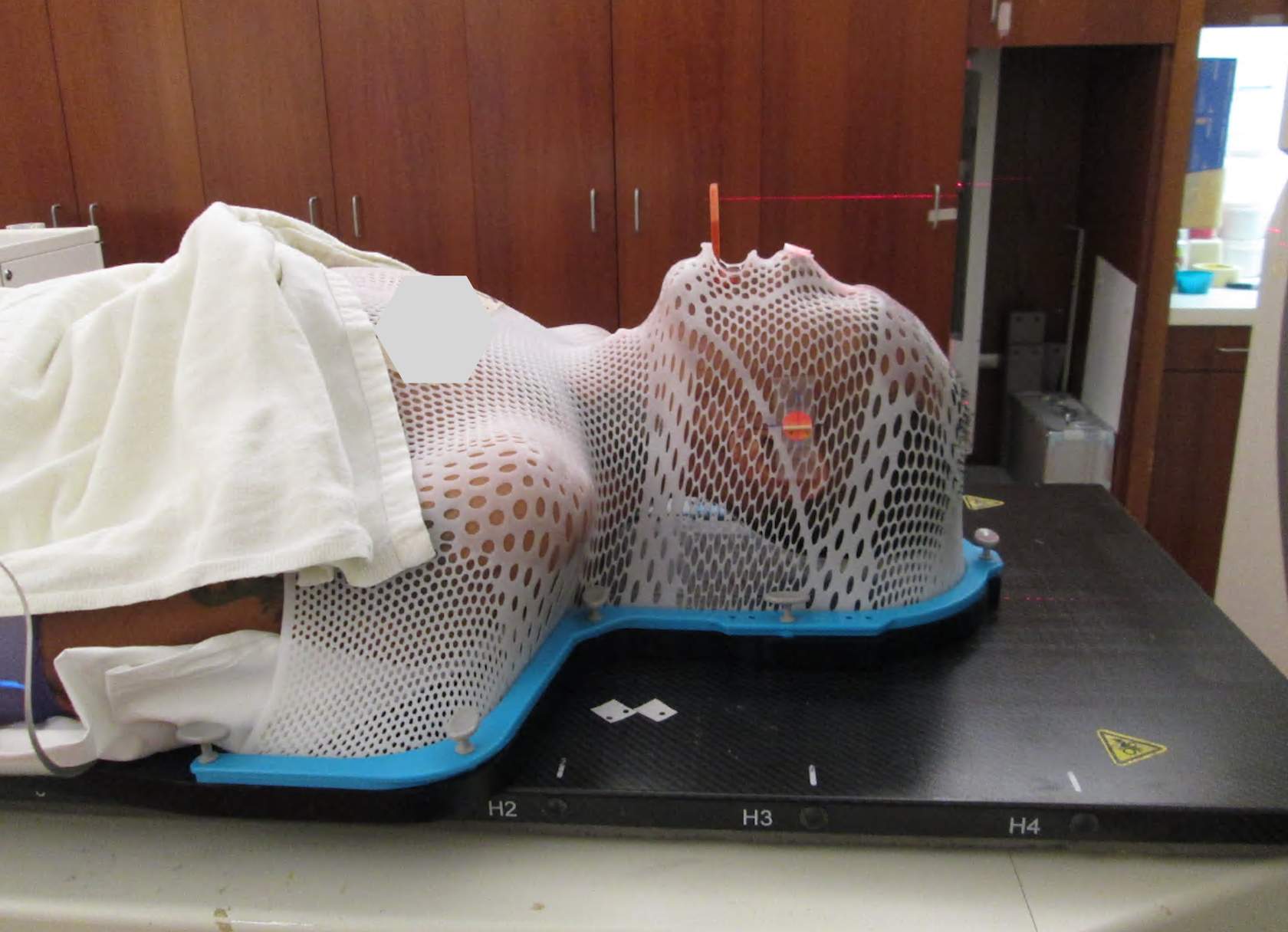
A Five-Point Mask, Reinforced Along the Chin
A five-point mask, reinforced along the chin, may be used to assist with shoulder placement. This is not typically necessary for WBRT.


Next: Import and Contouring

